What Types Of Uterine Fibroids Are There?
Four types of uterine fibroids may form in the uterus: intramural, pedunculated, submucosal, and subserosal fibroids. Women can one or more types of fibroids at any time. Each type may cause different symptoms
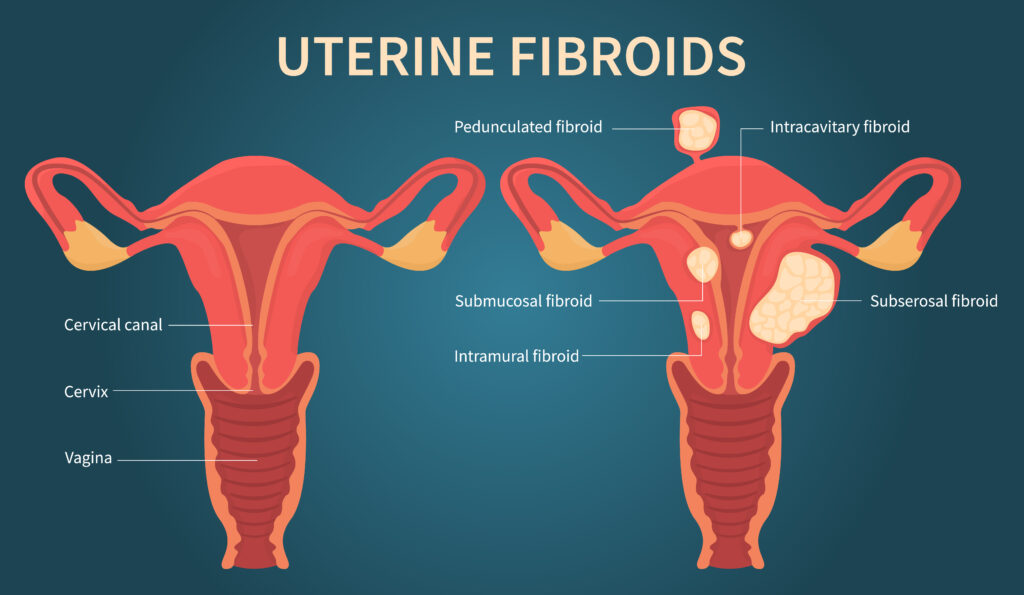
Intramural Fibroids
Intramural fibroids are the most common fibroids found in the uterus. These fibroids grow in the uterine wall and can grow to very large sizes if left untreated. Some women have many intramural fibroids growing in the same region. Pelvic or lower back pain and abnormal bleeding may result from this fibroid type.
Pedunculated Fibroids
Pedunculated fibroids grow from stem-like structures (peduncles) and form on the wall of the uterus or inside the cavity of the uterus. Quick movements may cause the peduncle to twist and cut blood flow, resulting in intense pain.
Submucosal Fibroids
Submucosal fibroids, the rarest type of fibroid, form under the uterine lining where they may crowd the uterine cavity. This type of fibroid may cause excessive bleeding and other significant complications.
Subserosal Fibroids
Subserosal fibroids grow on the outer uterine wall. Large growths in this region can crowd nearby organs and cause discomfort or pain.
What Are the Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are very common, and many women do not know they have them. Many women do not have symptoms or do not notice the signs. The location, size, and the number of fibroids present may influence whether or not you experience symptoms. Some of the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
- Constipation
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Frequent urination
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Leg pain
- Lower back pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Spotting between periods
Any of the symptoms above warrant a trip to your doctor. If you experience any sharp pain in your pelvic region or have severe vaginal bleeding, please seek immediate medical attention.
What Are the Risk Factors for Uterine Fibroids?
Although the precise cause for fibroids remains a mystery, there are a few risk factors that seem to be at play. Any one or more of the following factors could increase your chances of developing fibroids:
Hormones
Uterine fibroids are linked to the hormones estrogen and progesterone—two distinctly feminine hormones. The hormonal connection with fibroids is why nearly all women experience them at some point in their lives. For premenopausal women, these two hormones signal the uterine lining to prepare for pregnancy every month.
Genetics
If someone in your family has a history of uterine fibroids, there is an increased chance that you will also develop them. Researchers have found that women who develop fibroids have variations in a set of genes associated with the female reproductive organs.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body has a surge of estrogen and progesterone, the quintessentially female hormones mentioned above. As a result, getting pregnant could increase your risk of developing fibroids.

Uterine Fibroid Embolization Quiz
Find out if you’re a candidate for uterine fibroid embolization, a aminimally invasive procedure to treat fibroid tumors of the uterus. Answer a few quetions, get your results, and get in touch with Zenith Vascular & Fibroid Center for your consultation!
